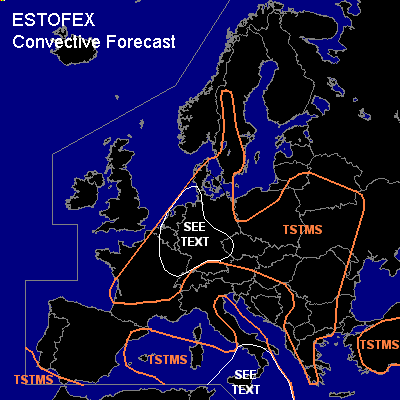

CONVECTIVE FORECAST
VALID 06Z MON 03/05 - 06Z TUE 04/05 2004
ISSUED: 03/05 00:45Z
FORECASTER: GROENEMEIJER
General thunderstorms are forecast across the western and central Mediterranean Sea
General thunderstorms are forecast across much of northwestern continental Europa and central Europe
General thunderstorms are forecast across parts of the Balkans
General thunderstorms are forecast across Turkey
General thunderstorms are forecast across parts of southern and central Sweden
SYNOPSIS
Monday at 06Z... an cut-off low is located over eastern Spain. A cold front located approximately along a line from the Baleares southward is expected to move eastward rapidly reaching southern Italy around or just after midnight Z. A southwesterly jet over Algeria is moving northeastward reaching the central Mediterranean at the end of the forecast period. A mid/upper trough is located over the eastern British Isles/ North Sea. A very strong 75 m/s northwesterly mid/upper jet is moving southeastward over the Atlantic.
DISCUSSION
...Western Europe...
An moderate strong southwesterly upper jet on the northeastern flank of the Spanish low pressure system is moving northeastward into central Europe. Weak DCVA-related rising motion in combination with solar heating is expected to cause destabilisation. MLCAPE values in the 500-1000 J/kg range are expected. 10-15 m/s of deep-layer shear is forecast in most places favouring the development of multicells. GFS 18z forecasts an increase in mid-level flow within the area marked "see text", so that deep-layer shear may approach 20 m/s. Particularly within this area a few isolated large (2 - 4 cm) hail events can be expected.
...Southern Italy...
As the front approaches southern Italy the associated jet overspreads the region creating about 30 m/s 0-6 km bulk shear and strong s.r.-helicity. Marignal surface-based latent instability is expected to form as a Saharan
elevated mixed layer in advected northward over the region. However, it seems likely that only some elevated convection will form as convective inhibition will probably prove to be too strong for surface-based convective development.
As shear within the elevated layer will still be around 20 m/s. A few elevated supercells will however still be possible with a main threat of large hail.
#